Milan#
(/mɪˈlæn/ mil-AN, US also /mɪˈlɑːn/ mil-AHN, Milanese: [miˈlãː] ⓘ; Italian: Milano [miˈlaːno] ⓘ) (From Wikipedia)
A city in northern Italy, regional capital of Lombardy, the largest city in Italy by urban population and the second-most-populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city has 3.22 million residents. The urban area of Milan is the fourth-most-populous in the EU with 6.17 million inhabitants. According to national sources, the population within the wider Milan metropolitan area (also known as Greater Milan) is estimated between 7.5 million and 8.2 million, making it by far the largest metropolitan area in Italy and one of the largest in the EU. Milan is the economic capital of Italy, one of the economic capitals of Europe and a global financial centre.
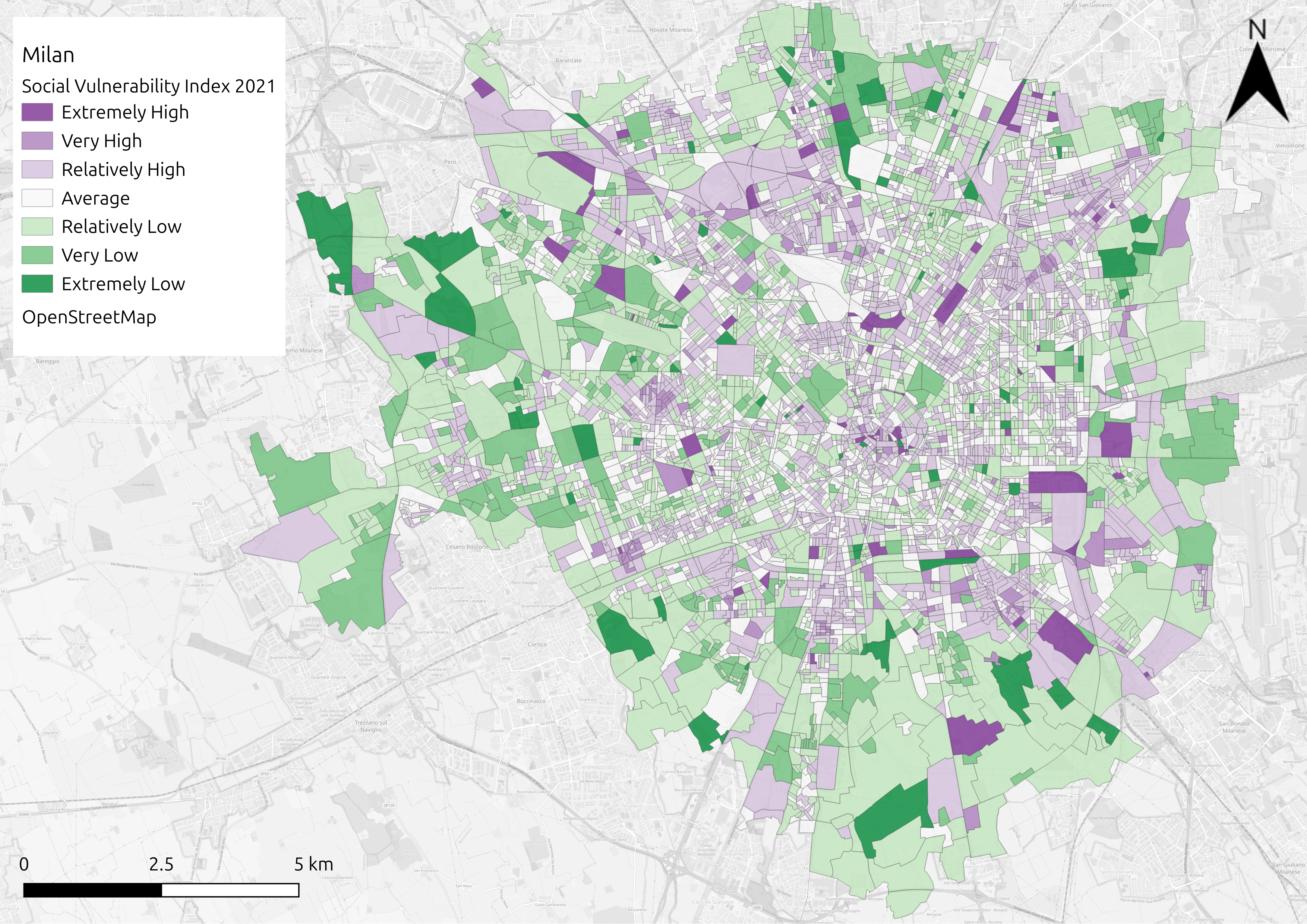
Indicators available in Milan, Italy, to determine vulnerability to extreme heat (taken from the national census for Italy and from European Copernicus datasets on land cover).
Indicator |
Domain |
Dimension |
Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
Boys under 5 years of age |
Age |
Sensitivity |
Physiologically, the young have a greater susceptibility to the effects of extreme heat. |
Girls under 5 years of age |
Age |
Sensitivity |
Physiologically, the young have a greater susceptibility to the effects of extreme heat. |
Males over 75 years of age |
Age |
Sensitivity |
Physiologically, older people have a greater susceptibility to the effects of extreme heat. |
Females over 75 years of age |
Age |
Sensitivity |
Physiologically, older people have a greater susceptibility to the effects of extreme heat. |
Dependents rate |
Income |
Adaptive Capacity – Ability to Prepare/Respond/Recover |
People with dependents may struggle to respond to and recover from extreme climatic events |
Unemployment |
Income |
Adaptive Capacity – Ability to Prepare/Respond/Recover |
Unemployed persons are more likely to have less incomes, and have limited ability to make physical adjustments to their property to adapt to extreme heat |
Population with no higher education |
Information Access/Use |
Adaptive Capacity – Ability to Prepare/Respond/Recover |
People with no formal education may find it difficult to interpret and/or act up on information received |
Percentage of foreign nationals |
Local Knowledge |
Adaptive Capacity – Ability to Prepare/Respond |
Foreign nationals are likely to have less local knowledge and be less aware of hazards |
Primary school age children |
Social Network |
Adaptive Capacity – Ability to Respond/Recover |
Those with primary school age children tend to have a stronger social network that can assist them during a heatwave event |
Households with one person |
Social Network |
Adaptive Capacity – Ability to Respond/Recover |
Those living alone likely lack a support network that can assist them during a heatwave event |
Impervious surface |
Physical Environment |
Enhanced Exposure |
Increased area of impervious surface enhances the urban heat island affect |
Tree cover |
Physical Environment |
Enhanced Exposure |
Increased area of tree cover and greenspace reduces the urban heat island affect |